
Imagine starting an assignment with focus and a clear structure, only to find your thoughts scattering as you bounce between tasks. Impulsivity leads to haphazard work, the clock keeps ticking, and by evening you’ve barely completed anything. You genuinely try to concentrate, but your brain feels exhausted.
This isn’t laziness or avoidance—it could be a sign of ADHD.
When you finally search for solutions, the advice can be overwhelming. Some recommend seeing a psychiatrist, while others insist on a psychologist. What should be a path toward clarity often becomes confusing.
So, can a psychologist diagnose ADHD, or do you need a psychiatrist? If you’re asking this question, you’re not alone.
Both psychiatrists and psychologists play vital roles in mental health care. One prescribes medication, while the other specializes in therapy and behavioral strategies. Understanding their differences can help you make an informed decision. In this blog, we’ll break down their roles, the ADHD diagnosis process, and treatment options—so you can choose the right professional for your needs.
| Professional | Can Diagnose ADHD? | Typical Role in Diagnosis | Treatment Involvement |
| Psychologist | ✅ Yes | Conducts psychological testing and behavioral assessments | Provides therapy and behavioral interventions |
| Psychiatrist | ✅ Yes | Medical diagnosis, may rule out other conditions | Prescribes medication and monitors response |
| Pediatrician / Primary Care Doctor | ⚠️ Sometimes | Initial screening, may refer to specialists | May manage medication if trained |
| Neurologist | ⚠️ Sometimes | Initial screening, may refer to specialists | Limited role in behavioral treatment |
Understanding ADHD: Why It’s Hard to Pin Down
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects attention, self-control, and activity levels. It often shows up differently in each individual, which is why misdiagnosis or overlooked symptoms are common.
- Children often display hyperactivity, fidgeting, or behavioral challenges.
- Adults may experience restlessness, emotional instability, procrastination, or difficulty focusing.
Because ADHD symptoms overlap with anxiety, depression, or even trauma, it can be hard to distinguish from other conditions.
According to the American Psychiatric Association, there are three main types of ADHD:
- Inattentive Type – Trouble concentrating, staying organized, or remembering tasks.
- Hyperactive/Impulsive Type – Restlessness, excessive talking, fidgeting, or acting without thinking.
- Combined Type – A mix of inattentive and hyperactive symptoms.
These shifting patterns can significantly affect daily life, making it important to seek an accurate evaluation.
Why People Get Confused: Psychologist vs. Psychiatrist
It’s easy to assume medication equals psychiatrist and therapy equals psychologist. While partly true, this oversimplifies their roles. Both professionals can diagnose ADHD, but they do so with different approaches and strengths.
Who Is a Psychiatrist and What Do They Do?
A psychiatrist is a medical doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating mental health conditions. They can prescribe medication and often create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your medical history, co-existing conditions, and symptoms.
Benefits of consulting a psychiatrist for ADHD include:
- Monitoring the effectiveness of ADHD medications.
- Managing co-occurring conditions like anxiety, depression, or bipolar disorder.
- Helping stabilize brain function through medical interventions.
- Providing insights into the connection between physical and mental health.
Who Is a Psychologist and What Do They Do?
A psychologist holds a doctoral degree in psychology and focuses on diagnosing and treating mental health conditions through non-medical methods. They cannot prescribe medication in most regions, but they provide comprehensive ADHD assessments using structured tests, behavioral evaluations, and in-depth interviews.
Benefits of consulting a psychologist include:
- Distinguishing ADHD from other conditions with overlapping symptoms.
- Teaching coping strategies for stress, organization, and focus.
- Identifying emotional triggers and building healthier responses.
- Supporting both mental and physical well-being.
- Offering therapy options, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), to replace unhelpful thought patterns.
How ADHD Is Diagnosed: Step by Step
| Step | Description | Who Performs It |
| 1. Clinical Interview | Discussion of symptoms, history, and daily challenges | Psychologist / Psychiatrist |
| 2. Behavioral Assessment | Use of rating scales (e.g., Conners, Vanderbilt) | Psychologist |
| 3. Observation & Testing | Cognitive and attention tests (e.g., CPT) | Psychologist |
| 4. Medical Evaluation | Rule out physical conditions | Physician |
| 5. Feedback & Diagnosis | Final diagnosis and treatment plan | Psychologist / Psychiatrist |
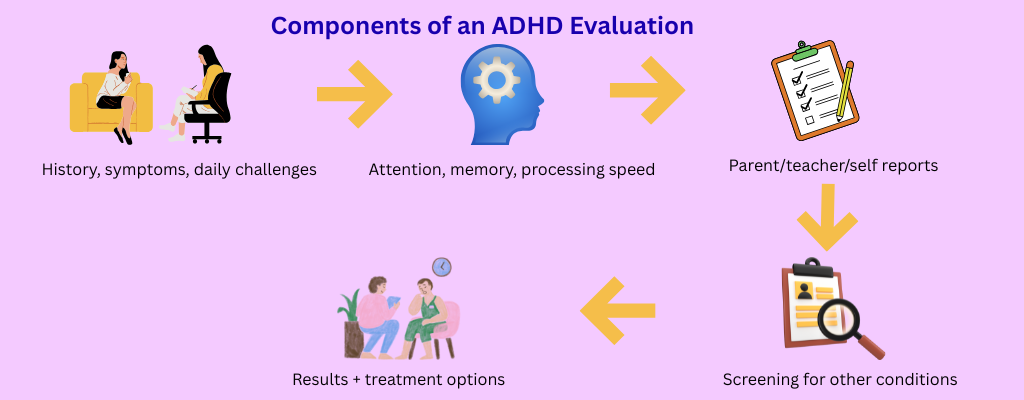
Since ADHD often coexists with other conditions, diagnosis can be complex. Psychiatrists, psychologists, and in some cases therapists all use structured approaches to ensure accuracy.
1. Initial Diagnostic Interview – A 1–2 hour session covering childhood history, family background, lifestyle, and specific struggles.
2. Family Interviews – Input from parents, partners, or old school records helps confirm whether symptoms existed before adulthood.
3. Standardized Assessments – Screening tools such as the ADHD Self-Report Scale or Conners’ Rating Scales evaluate attention span, behavior, and co-occurring conditions like anxiety or depression.
4. Medical Tests – Since thyroid issues or seizure disorders can mimic ADHD, doctors may order medical or neuropsychological tests to rule out other causes.
5. Feedback Session – After assessments, you’ll receive a diagnostic report with results, explanations, and treatment recommendations.
Symptoms to Watch For
ADHD affects roughly 60% of adults who had it in childhood, though many go undiagnosed due to overlapping symptoms with stress or other mental health conditions.
1. Inattention
- Difficulty concentrating or staying on task
- Forgetfulness and disorganization
- Losing important items frequently
2. Impulsivity
- Speaking or acting without thinking
- Interrupting conversations
- Struggling to wait your turn
3. Hyperactivity
- Restlessness and fidgeting
- Excessive talking or excitement
- Trouble staying seated or quiet
Effective ADHD Treatment Options
While ADHD cannot be “cured,” it can be managed successfully with the right treatment plan. Approaches often include a mix of medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
1. Medications
- Stimulants (e.g., methylphenidate, amphetamines) increase dopamine and norepinephrine to improve focus and calm hyperactivity.
- Non-stimulants (e.g., atomoxetine, certain antidepressants) may be prescribed when stimulants are ineffective or cause side effects.
2. Psychological Counseling
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps restructure negative thought patterns and improve coping strategies.
Talk therapy builds self-awareness, relationship skills, and frustration tolerance.
3. Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise, mindfulness, or yoga to sharpen focus.
- Digital reminders, planners, and quiet environments to improve productivity.
- ADHD support groups to share strategies and gain encouragement.
Snead Psychological Services: Choosing the Right Professional for ADHD
So, can a psychologist diagnose ADHD, or do you need a psychiatrist? The answer is that both are qualified—but in different ways. Psychiatrists focus on medical treatments, while psychologists provide behavioral strategies and therapeutic support. For many, the best approach combines both.
If ADHD has left you feeling scattered or overwhelmed, don’t let it define your life. At Snead Psychological Services, we provide thorough assessments and tailored therapies to help you move forward with confidence.

